The discovery of plasma arc revolutionized the speed and accuracy of cutting. It enabled manufacturers to make different types of cuts in all types of metals. There are numerous advantages of plasma cutters such as high precision, cutting capacity, speed and productivity, lower operating costs and versatility. Plasma cutters can handle any electrically conductive metal and also handle expanded metal – rusted and most painted surfaces (subject to a good bare metal earth contact). In the plasma cutting process you don’t need to preheat the metal before cutting therefore saving you time and faster speeds can be achieved with certain metals, with minimal or no metal distortion. Plasma cutters also have safety advantages compared to other cutting systems because they do not require the use of flammable gasses. It is also widely acknowledged that plasma cutters are relatively simple to use compared to other cutting systems like the oxy-fuel cutting systems.
What is a Plasma Cutter?
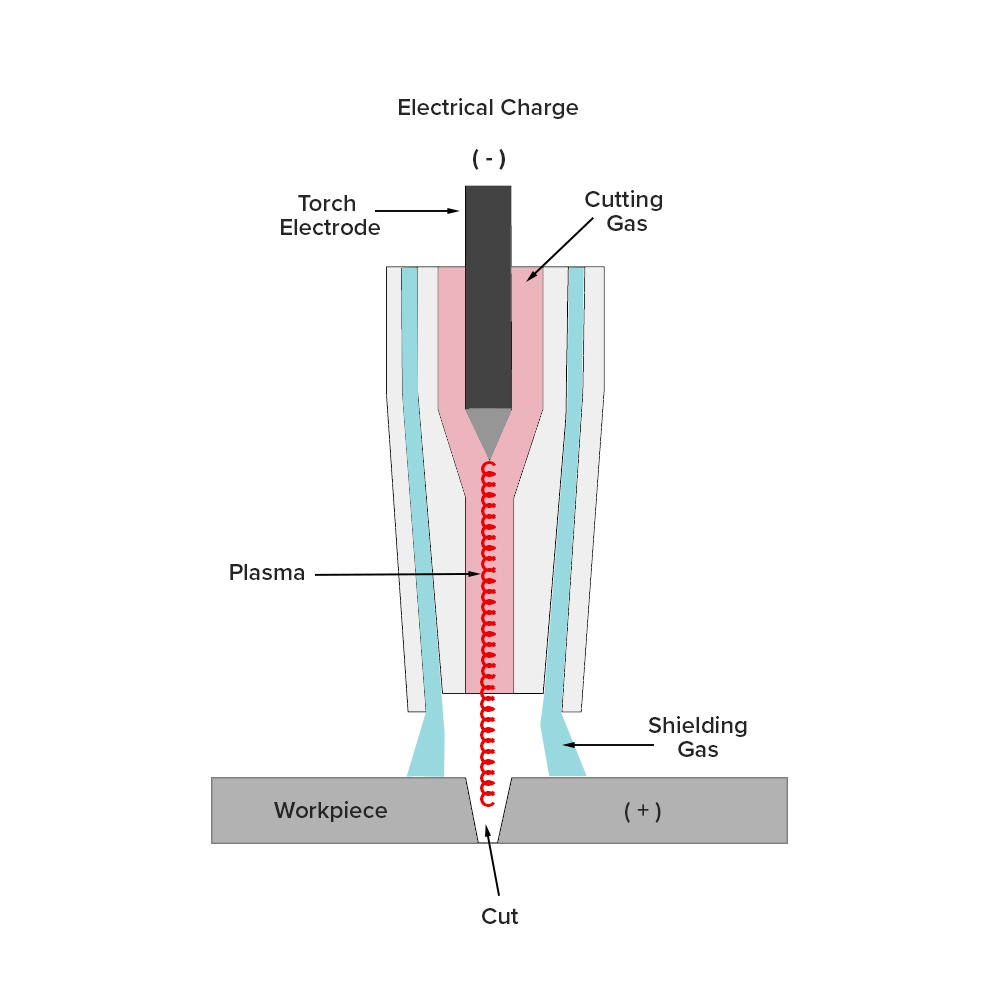
Plasma is the fourth state of matter. You may be already aware of the first three: solid, liquid and gas. With the introduction of heat, you can change the state of a matter from solid, to a liquid, to a gas, and then to a plasma. The difference between gas and plasma is that plasma is electrically conductive, in other words plasma is ionized gas. When the gas is heated to extremely high temperatures, you will get plasma. The high temperature speeds up the movement of the electrons. The fast-moving electrons collide with other electrons and ions. Their collision results in the release of vast amounts of energy. That energy is what gives plasma its unique status and extreme cutting power.
Plasma cutting machines simply harness the power of plasma to cut metals. Plasma cutters work by creating a high temperature electrical channel of plasma (ionized gas), this plasma stream is then used to cut ferrous and non-ferrous materials.
Plasma cutters come in all shapes and sizes. There are big plasma cutters known as CNC Plasma Cutters that use a plasma torch with robotic arms controlled by a computer to make precise cuts. Thanks to technological advances, plasma cutters have now become portable. There are handheld and portable plasma cutters allowing users to cut freehand as needed.
How does a Plasma Cutter Work?
Plasma cutters work by sending electrical current, via a negatively charged electrode, through a narrow opening which heats the gas to an extremely high temperature creating a plasma stream. Plasma cutters apply power to the negative electrode and when the torch is moved closer to the material the plasma will transfer directly to the metal creating temperatures in excess of 16,000°C, easily cutting the work piece.
How to choose the right Plasma Cutter?
There are certain things you need to know before you choose a plasma cutter. It is more than just the cutting capacity, you need to consider the material type and thickness of what you want to cut. The power you have available in your workplace may also determine which type of machine (110V, single phase 240V or 3 phase 415V). The most common Plasma cutters require compressed air and some are available with a built-in compressor. Depending on the machine’s cutting capacity, it will require a specific CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) to supply the machine. There are other factors as well.
See our Guide to Choosing the Right Plasma Cutter
What gas is used for Plasma Cutters?
In order to create the plasma used for cutting, a gas is required. The most common gasses used by plasma cutters are compressed air, oxygen, nitrogen, argon and hydrogen/argon mix. The correct gas for a plasma cutter will depend on what the machine is designed to use and the type of material you are cutting.
Compressed air is mainly used for hand cutting machines. It is the most versatile and the most economical of all the plasma gasses as it is freely available. Compressed air is commonly used for low current cutting and is suitable for mild and stainless steel as well as Aluminium and carbon steel for plasma gouging.
Oxygen is mostly used in CNC machines, offers the fastest cutting speed compared to other plasma gasses while simultaneously offering the best cut quality. One benefit of using oxygen plasma is that the air acts as a shielding gas. It is suitable for carbon steel with thicknesses of up to 1 – ¼ inch. Oxygen can also be used on stainless steel and Aluminium but the quality may lack as it produces a rougher cut surface.
Nitrogen Provides the hottest burning plasma. It may be expensive but it is recommended for high-current plasma cutters and is suitable for mild and stainless steel or Aluminium up to 3 inches thick.
Argon-Hydrogen is a mix of 65% argon and 35% hydrogen gas. It is suitable for cutting any material above 3 inches. This mix produces the hottest plasma for cutting through materials and for this reason it produces an excellent quality cut on stainless steel and Aluminium. However, for the same reason it is not recommended for cutting mild steel.
Engweld supplies various types of Gasses under its brand name Energas
The table below can help you in choosing the best gas for plasma cutting (mostly CNC machines).
| Plasma Gas & Shield | Mild Steel | Stainless Steel | Aluminium |
| Air & Air | – Excellent cut quality- Faster cutting speed- Cost-effective | – Nice cut quality- Faster cutting speed- Cost-effective | – Nice cut quality- Faster cutting speed- Cost-effective |
| Oxygen & Air | – Excellent cut quality- Faster cutting speed- Very little dross | – Not recommended | – Not recommended |
| Nitrogen & Air | – Fair cut quality- Impressive parts life- A little dross | – Good cut quality- Impressive parts life | – Excellent cut quality- Impressive parts life |
| Nitrogen & CO2 | – Fair cut quality- Impressive parts life- Little dross | – Good cut quality- Impressive parts life | – Impressive parts life- Good cut quality |
| Nitrogen & Water | – Fair cut quality- Impressive parts life- A little dross | – Excellent cut quality- Impressive parts life | – Excellent cut quality – Impressive parts life |
| Argon-Hydrogen & Water | – Not recommended | – Perfect for thickness > ½” | – Perfect for thickness > ½” |
Plasma Cutting Consumables
Like many other machines, plasma cutter consumables are the components of the plasma cutter that have a life cycle. They wear out over time and they need to be replaced to ensure your machine’s performance, efficiency and durability. Consumables in a plasma cutter are mainly found in the torch because that is where most of the work takes place. Plasma cutting torch consumables are swirl ring, electrode, nozzle, retaining cap and shielding cap. It is important to keep an eye out on your nozzle and electrode as they will wear out more quickly than the others because they are directly involved in the creation and focussing of the cutting arc. One sign to look out for the wear of a nozzle will be the quality of the cut.
Engweld stocks a wide range of plasma cutter consumables including Plasma Torches and Spares
Swirl Ring
Electrode
Nozzle
Retaining Cap
Shielding Cap
How can you prolong the life of Plasma Cutting consumables?
You can prolong the life of your plasma cutter consumables by following some simple guides. Make sure you are not cutting too quickly, too slowly or at the wrong distance from your work piece. Make sure your components are installed correctly. For example, the tolerances of the consumables should match the amperage you will be using. Keeping track of the components wearing and ensuring their timely replacement to prevent one worn out component reducing the life cycle of other components as they all work together hand in hand.
Please Note: Some machines have an expanded metal or wire mesh cut option. Using this on solid materials will vastly reduce your consumables life.
What is Plasma Gouging?
Plasma gouging is a variation of plasma cutting. It is similar to plasma cutting in the sense that a plasma arc is formed between the negatively charged electrode and the positively charged work piece. The high speed plasma jet blows the molten material away resulting in a cut. However, in plasma gouging you don’t completely cut the material. Some of the metal on the surface of the work piece is melted and the molten metal is blown away by a gas jet from the work piece. In a nutshell, plasma gouging is a process that removes some of the metal from the work piece by using a plasma arc between the torch and the work piece.
There are various different techniques to achieve different gouge profiles and sizes. One popular technique is by holding the plasma torch at a 35 to 40 degree angle to the work surface while the pilot arc is formed and transferred to the plate. Once the contact is achieved, the operator then feeds the arc into the gouge or in the direction they want to gouge. Steeper angles combined with slower speeds will allow the arc to penetrate more deeply into the workpiece. Smaller angles with faster speeds will remove less material thus producing a shallower gouge.
You can gouge with the plasma cutting system but to avoid accidentally cutting through the workpiece and achieve quality, it is recommended that you use gouging-specific shields and nozzles. There are special gouging consumables that produce a wider and softer arc.
Engweld supplies various plasma gouging consumables.
Can all Plasma Cutters gouge?
Most modern plasma cutters are capable of cutting and gouging as well. You may only need to change the parts on your plasma cutter torch when doing plasma gouging.
How to cut perfect circles with your Plasma Cutter?
You can cut perfect circles with a circle cutting kit. The kit comprises parts that need to be attached to the nozzle of the plasma cutter. Find the center of your circle and center punch or drill a small hole to allow the centering pin to sit into or attach through the sheet metal with.
ESAB Handyplasma Circle Cutting Guide Kit
How to cut a straight line with a Plasma Cutter?
If you have any questions about plasma cutting or want to find out more, please contact us and speak to one of our experts.