Choosing the right tool for the job is critically important to the success of the project. This guide will give you a better understanding of flap discs and help you choose the right one for your application.
What are flap discs?
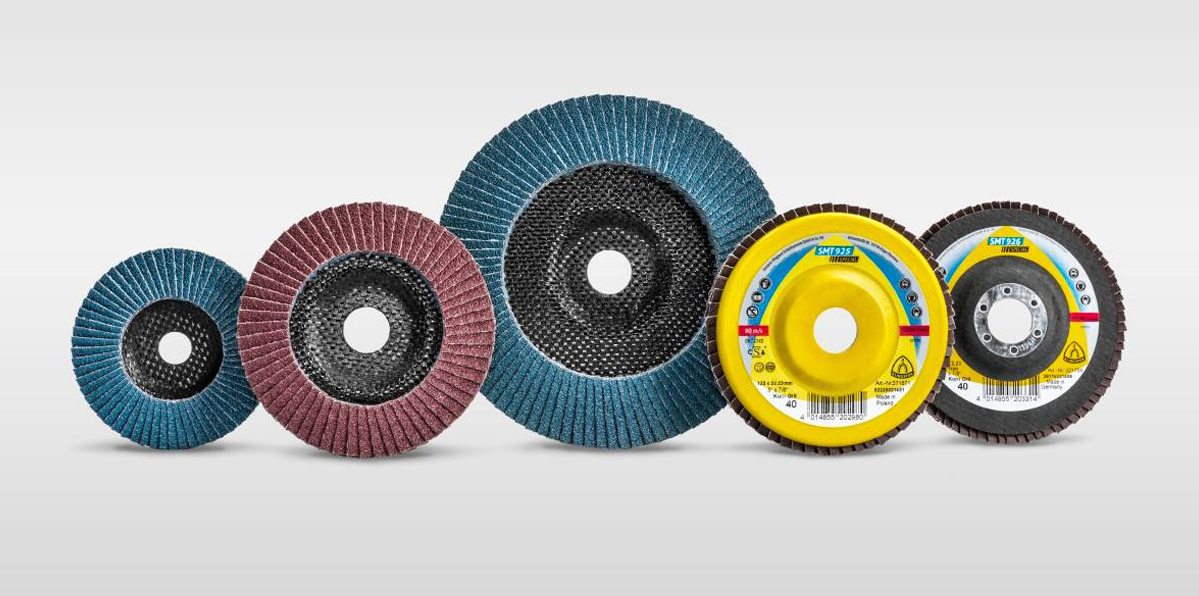
A flap disc, also known as abrasive mop disc, is an abrasive disc used for contouring, conditioning, and shaping metals. It consists of a backing plate with multiple overlapping abrasive flaps arranged in a circular shape. The abrasive material used on the flaps can vary, but common options include aluminium oxide, zirconia alumina, and ceramic. The abrasives are attached to a backing cloth made of either polyester, cotton, or blended material. The backing plate may be made of plastic, fiberglass, or metal.
Flap discs are preferred for several reasons. They are lighter, easier to control, and with long application life require less changing meaning less downtime, less vibration, and reduced noise.
Flap discs are attached to a power tool like an angle grinder using a specific attachment mechanism. The exact attachment method may vary depending on the design of the angle grinder and the type of flap disc.

What are flap discs used for?
Flap discs are used for grinding, blending, and finishing applications. They are widely and commonly used in metal fabrication, and all other association sub-sectors. Flap discs are versatile and can be used on various metal types for grinding, deburring, surface blending, surface preparation, finishing and polishing, shaping and beveling, and stock removal.
Coated abrasive flap discs are an essential component to improve the appearance and quality of the finished product making them popular in various industrial environments, as well as for DIY projects. Some of the common applications for flap discs include cleaning flash molds and castings, removing rust, edge grinding, deburring, and blending weld seams.
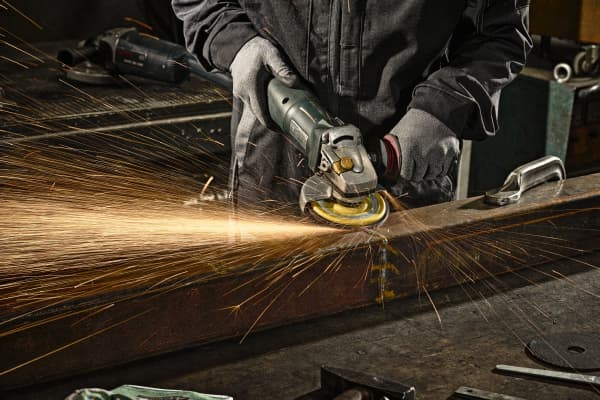

How to use a flap disc?
Flap discs are a type of abrasives and fall under the scope of PPE regulations. When using flaps discs, wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) including safety glasses/goggles, a face shield, ear protection, and work gloves. It is also important to make sure your angle grinder must have a guard positioned between you and the disc. The guard is designed to protect you from an injury in case there is a breakage or flap separation during use.
To meet the safety standards specified in ‘Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations’, it is important to ensure that equipment is suitable for its intended use, properly maintained, and used safely. Always inspect the flap disc, backing pad, and angle grinder before and after use. Look out for any signs of damage and never use a damaged disc to avoid safety hazards. Store the flap discs in their original containers and keep them away from water or other fluids.
One of the most important factors in using flap discs is the angle. A flap disc must always be used at the correct angle to achieve the best results and to avoid wear or damage to the backing pad. The correct angle will also depend on the type of flap disc being used.
Flap discs should not be used flat or on the edge and avoid excessive pressure or angling the disc too steeply as it may cause uneven grinding or excessive wear on the disc. Move the flap disc smoothly across the workpiece surface, using even and consistent motions. Avoid dwelling in one spot to prevent excessive heat buildup or uneven finish.
Flap Disc Shapes
Flap discs come in different shapes to accommodate different grinding and finishing tasks, The two most common ones are flat discs and conical discs.
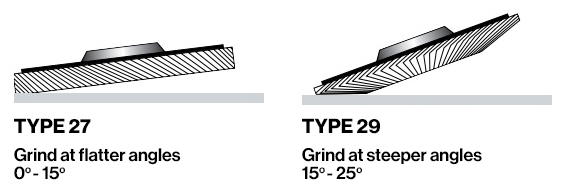
Flat discs – are also known as type 27. A type 27 flap disc should be used at 0°-15° angle to the workpiece.
Conical discs – are also known as type 29. Type 29 flap disc should be used at 15°-25° angle to the workpiece.
Convex Flap Discs: have a curved shape that is outwardly rounded. They are ideal for working on curved or concave surfaces, such as pipes and tubes. Convex flap discs conform to the workpiece’s shape, allowing for efficient material removal and blending without excessive stock removal.
Generally, a conical disc is used for initial grinding, especially on tough metals or when a considerable amount of grinding needs to be done. You can do some mild grinding with flat discs, but they are more suitable for doing the finishing on the workpiece. For applications requiring lower grinding pressure and more control, a flat shaped flat disc is recommended.
Flap Discs Abrasives
Flap discs have different types of abrasives, and each has its own characteristics making them suitable for specific applications. Each material has different properties in terms of aggressiveness, durability, and heat resistance. The right choice of abrasive will depend on factors such as materials being working, the desired finish, the level of stock removal required, and the operating conditions.
Ceramic: ceramic abrasives are made from a mixture of ceramic grains and other abrasive materials. Their unique crystal structures have self-sharpening characteristics, so it continually exposes the newly sharpened abrasives making them more efficient and productive. They are known for their exceptional cutting power, durability, and longevity. Ceramic abrasives are extremely hard and can withstand high grinding pressures and temperatures. They are suitable for heavy-duty applications where fast stock removal and aggressive cutting action are required, such as grinding hardened steels, titanium, super alloys, and other hard metals.
Zirconia Alumina: are synthetic abrasives made by fusing zirconium and aluminium oxide. They are known for their high strength and durability and are great for carbon and mild steel applications.
Aluminium Oxide: abrasives were one of the first to be used for flap discs. They are made from bauxite ore and undergo a refining process to produce abrasive grains of different sizes. They are not self-sharpening and are commonly used for general-purpose grinding, deburring, blending, and finishing operations on various metals.

Flap Disc Grits
The grit size determines the coarseness or fineness of the abrasive. The right grit size will depend on your application. Lower grit numbers indicate a coarser abrasive, suitable for heavy material removal, while higher grit numbers indicate a finer abrasive ideal for surface preparation and finishing.
Generally coarser flap discs with lower grit size are used initially on workpiece shaping and stock removal and the finer higher grit size flap discs are used for refinements such as blending, polishing, and finishing. The table below can help you choose the right grit for your application.
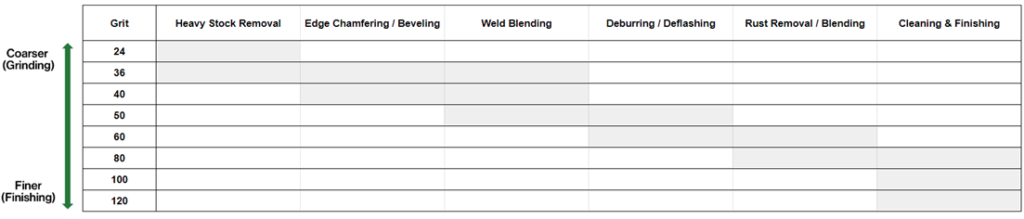
Typically, 24 to 60 grit range flap discs are coarse, while 60 to 80 grit range are medium, and 80 to 120 are considered as fine.
- 24 to 36 grit range is very coarse making them ideal for heavy duty operations such as heavy stock removal.
- 36 to 40 grit flap discs are coarse and suitable for edge work like chamfering and edge beveling.
- 36 to 50 grit range can be used for weld grinding and blending.
- 50 to 60 grit flap discs are medium, so they are recommended for deburring and deflashing applications.
- 60 to 80 grit range is fine and typically used for rust removal and blending.
- 80 to 120 grit flap discs are finer and well-suited for refining applications such as cleaning and finishing.
Flap Disc Density
Flap disc density refers to the number of abrasive flaps or layers present on a flap disc. The flap density can vary. Higher flap density generally means more flaps per square inch or centimeter, resulting in a greater number of cutting edges.
A flap disc with a higher density tends to offer a finer and more uniform finish, as the increased number of flaps provides cutting points and a larger contact area with the workpiece. It can be useful for applications requiring a smooth surface or finer material removal.
On the other hand, flap discs with lower flap density may be more aggressive, allowing for faster material removal but potentially leaving a rougher finish. They may be suitable for tasks where efficiency is prioritized over surface smoothness.
The selection of flap density depends on the specific application, the material being worked on, and desired finish.
Flap Discs vs Grinding Discs vs Fibre Disc
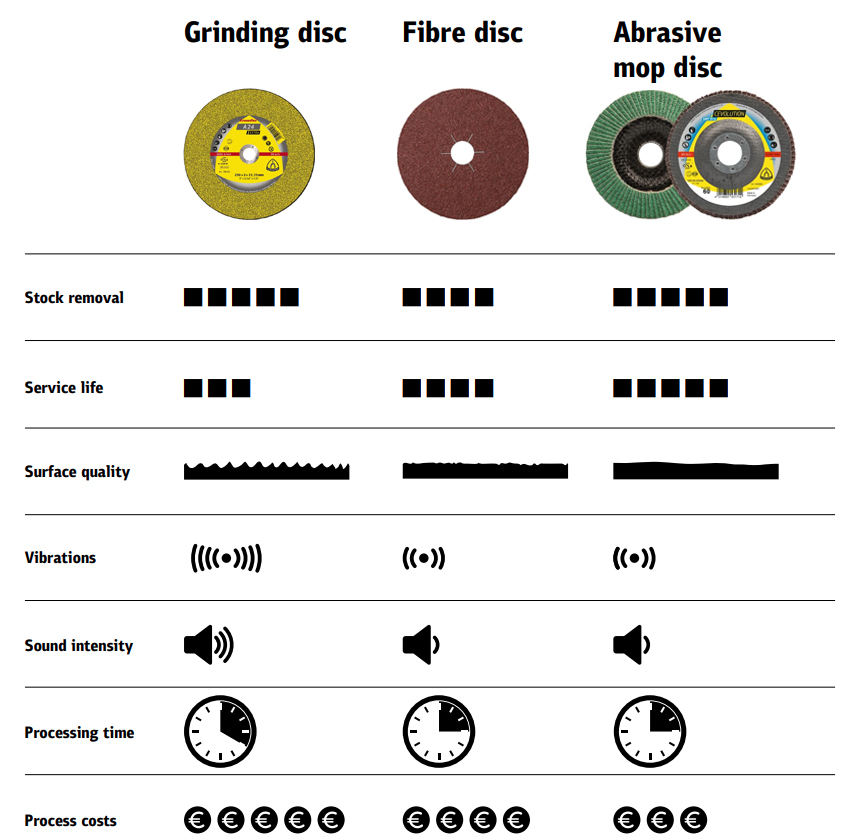
Flap discs, grinding discs, and fibre discs are all abrasive discs and similar in nature with overlapping characteristics, but they have crucial differences that define which one is suitable or unsuitable for certain applications. For example, the coarser nature of grinding discs results in an uneven finish making them unsuitable for surface preparation.
Flap discs also remove metal but at a slower pace than grinding discs, but they will give you a smoother and even finish. The flexible nature of flap discs makes it easier for you to achieve contours in the metal making them suitable for deburring, blending, and finishing. Advancements in design and technology over the years have made flap discs truly versatile to the point where they can be used for grinding, blending, and finishing jobs quickly and with less noise than grinding discs.
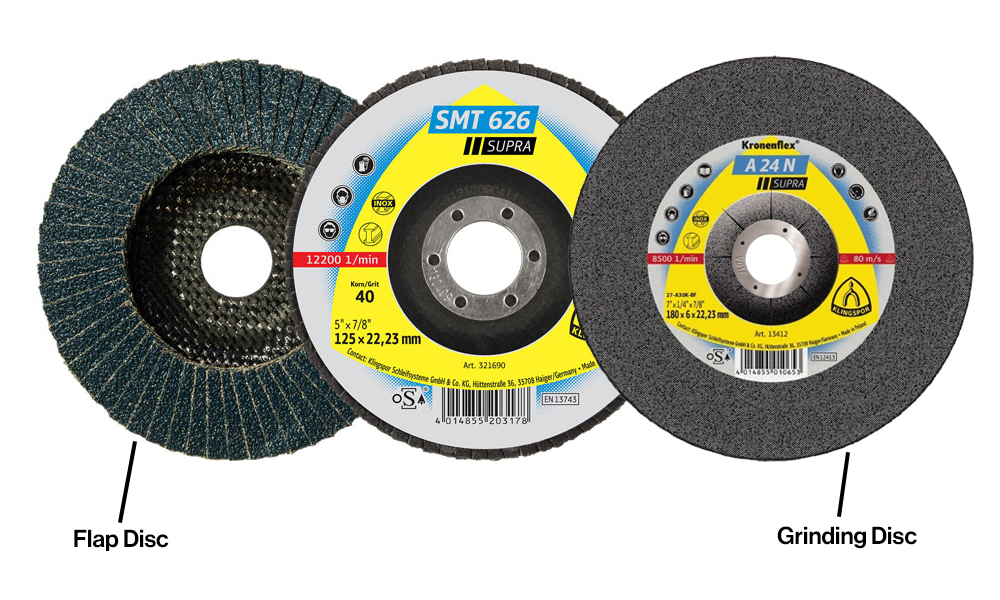

Fibre discs are grinding wheels with a backing made of reinforced vulcanised fibre that is coated on one side with resin and abrasive grain. They provide the benefit of less vibrations and less noise. They are also more flexible, which allows them to adapt to the surface.
To finish a weld seam, the welder can choose from grinding disc, fibre disc, and flap disc (abrasive mop disc). The table below from Klingspor compares the different properties of grinding disc, fibre disc, and flap disc. The right choice will depend on the application and what the user aims to achieve.
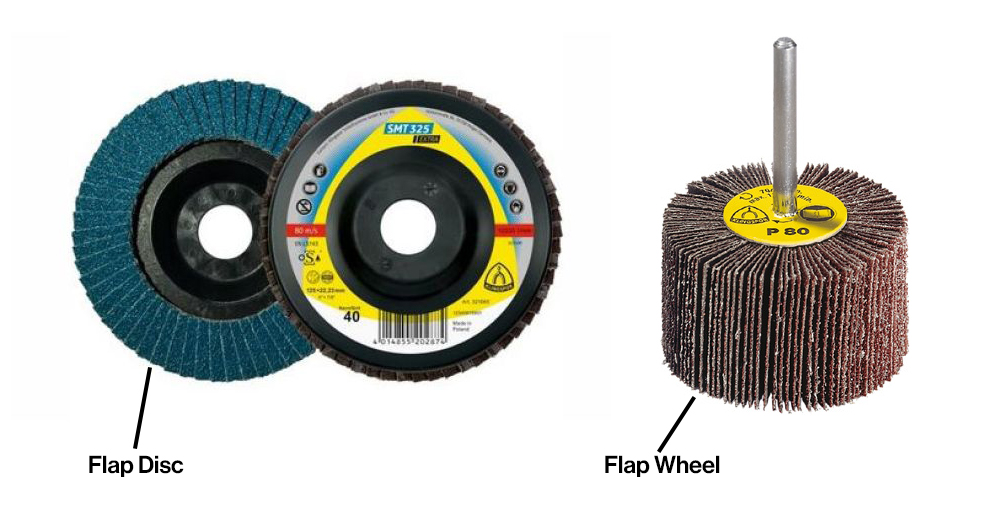
Flap Discs vs Flap Wheels
Flap wheels are abrasive tools used for grinding and finishing applications. They consist of a series of abrasive flaps that are arranged in a cylindrical shape around a central core or spindle.
Flap discs and flap wheels are both abrasive tools and serve the same purpose but there are some differences between them in terms of design and functionality. Flap discs have a flat design with some having a slight angle. Flap wheels have a cylindrical shape which makes them suitable for hard-to-reach areas such as curved or contoured surfaces.
Flap discs are generally more rigid due to their flat design, so they are more aggressive making them suitable for heavy stock removal. On the other hand, flap wheels can be more flexible allowing them to conform to the workpiece which makes them a better choice for contouring, polishing, and deburring applications, especially in hard-to-reach areas such as pipes.

If you have any questions and queries, please contact us. We have experts in abrasives who can guide you in choosing the right abrasive tool for your application.